Ryzen 7000 is extra than simply AMD’s newest batch of processors. The Ryzen 7950X, 7900X, 7700X, and 7600X are AMD’s first Zen 4 chips, first produced on 5nm, first to sport built-in graphics, and first to usher within the new AM5 socket with debut PCIe 5 and DDR5 assist.
As you’ll see in our Ryzen 9 7950X review, AMD has a lot to be happy with. Dig by means of the numerous benchmarks, and also you’ll see the flagship CPU trounce the competitors and publish massive enhancements over last-gen Ryzen 5000. The chips down the listing pull out some flashy numbers, too.
It provides as much as an excellent accomplishment for Team Red—although one set in opposition to a backdrop of sophisticated nuances. Here are the 6 important issues that you must find out about AMD’s excellent Ryzen 7000 CPUs.
The Ryzen 9 7950X is a multithreaded monster
Gordon Mah Ung / PCWorld
Got heavy rendering and/or encoding workloads? The Ryzen 9 7950X is the chip for you. It stomps Intel’s flagship Core i9-12900K in uncooked efficiency. In our multithreaded benchmarks, it gained time and again, with its smallest victory a hefty 37 p.c, and its largest a whopping 60 p.c. The 7950X exhibits up its predecessor, too, with its lead over the 5950X as massive as 48 p.c.
This chip’s weak spot (when you can name it that) is as a substitute in single-core and calmly threaded duties, and a few particular areas like machine studying and encryption. The battle with Intel is pretty even right here, with Team Blue’s flagship chip typically popping out on high. Add in software program optimization, like Adobe Premiere Pro’s use of QuickSync to spice up video enhancing duties, and the 12900Ok can outperform the 7950X in sure workloads. We’ll should see if Ryzen 7000’s built-in graphics end in related assist for Team Red and a extra even taking part in discipline sooner or later.
But that doesn’t imply Ryzen 7000 loses to 12th-gen Alder Lake exterior of multithreaded duties. Not in any respect. In truth, the least-powerful chip at launch, the Ryzen 5 7600X, can beat the 12900Ok in a variety of video games. What in the end issues are the software program and video games you employ most.
More energy, extra energy draw
Gordon Mah Ung / PCWorld
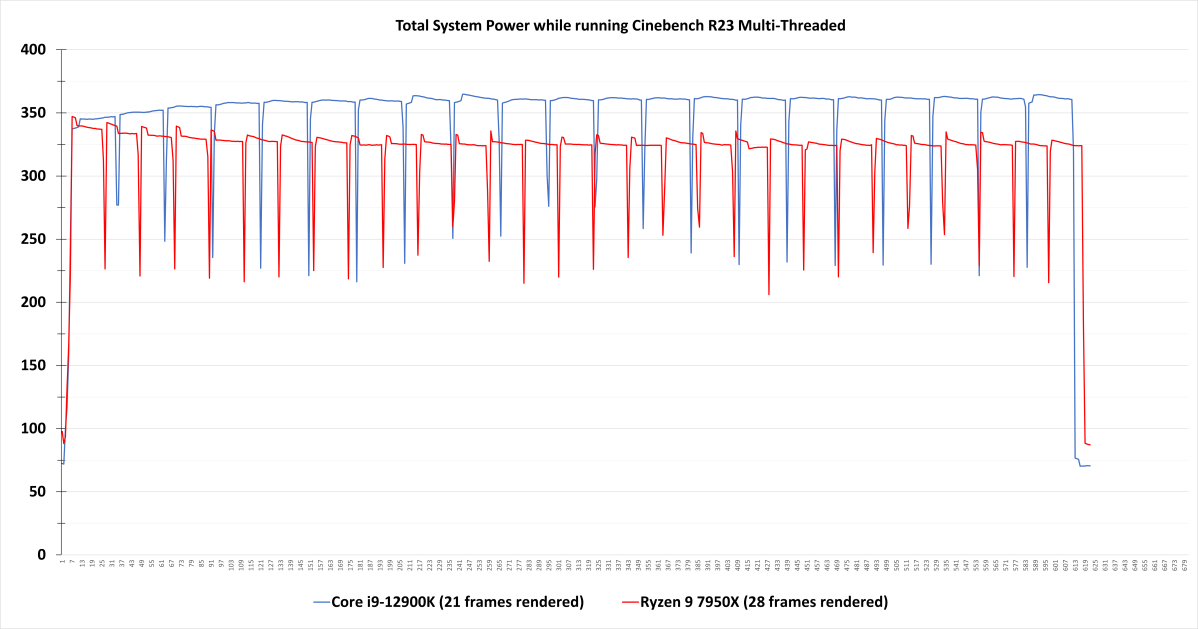
Ryzen 7000’s beautiful efficiency is partly a results of AMD upping electrical energy consumption. The new AM5 socket permits extra juice to movement to the processor, and this primary batch of suitable chips takes benefit of that.
So you may anticipate the next energy invoice when working one among these chips. The quantity is determined by how exhausting you push them in day by day use, however TDP offers common concept of the rise. The Ryzen 9 5950X is rated at 105 watts; the 7950X, 170 watts. That’s the anticipated energy draw beneath load—and it may well go up increased nonetheless throughout a efficiency enhance. Ryzen 7000’s restrict is 230W by means of its socket, whereas Ryzen 5000 caps out at 142W.
Why the change? Intel. It already took this identical route earlier than AMD. By altering its method (and design), AMD neutralizes that potential benefit.
Yet higher energy effectivity
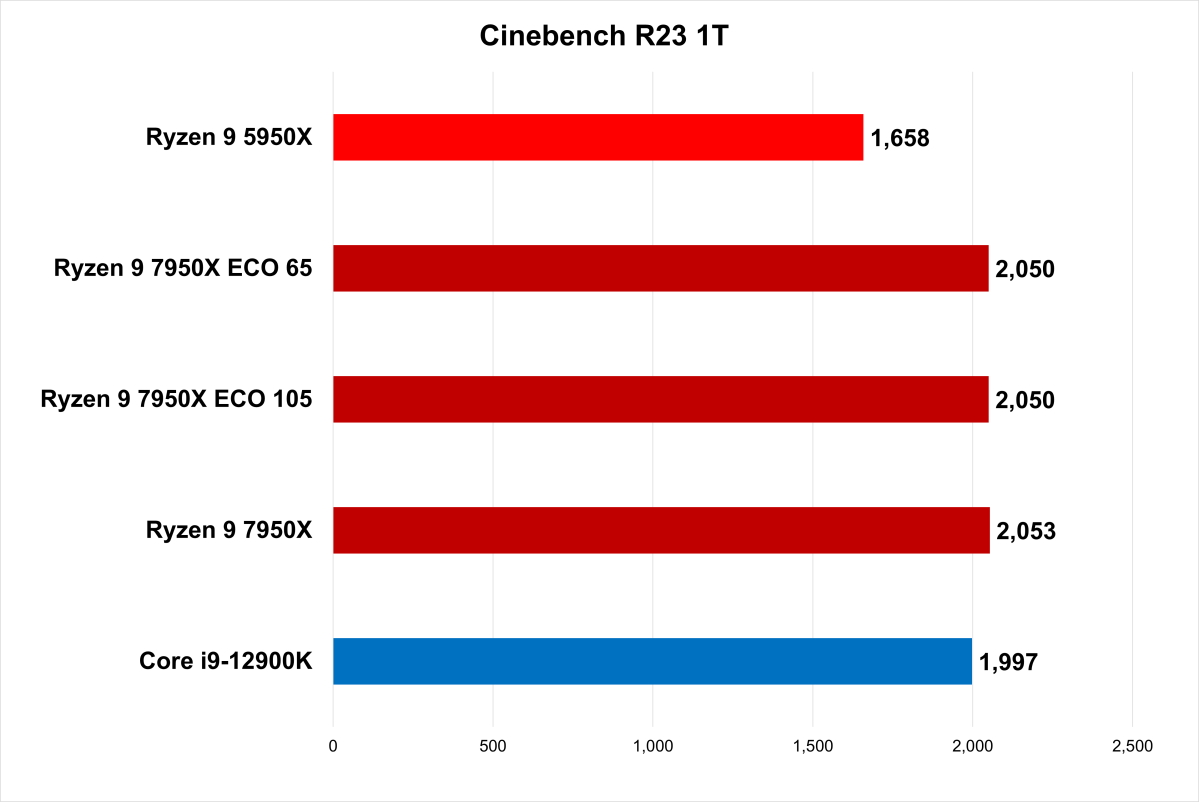
Performance on this single-core benchmark barely budged even when energy to the 7950X was restricted by greater than half. (Longer bars point out higher efficiency
.)
Gordon Mah Ung / PCWorld
When chips begin to use extra energy—as Ryzen 7000 does—the efficiency squeezed out of every watt turns into necessary, particularly given rising vitality prices worldwide.
Fortunately, Zen 4 delivers on the corporate’s claims of better energy effectivity. At least, the Ryzen 9 7950X did so in multithreaded duties. When in comparison with the Intel Core i9-12900Ok, it will get way more accomplished in the identical period of time, or just finishes sooner. The 7950X makes use of much less electrical energy whereas doing so, too.
It doesn’t win as clearly in single-core and calmly threaded duties—there, the 12900Ok usually beat the 7950X on vitality effectivity in our exams.
But AMD nonetheless has one other trick up its sleeve, and it’s referred to as Eco Mode. An straightforward change in AMD’s Ryzen Master software program utility permits you to restrict the ability working to Ryzen 7000 chips. For instance, the 7950X and 7900X can drop all the way down to from 170W to 105W or 65W. This settings tweak reduces electrical energy drawn, with surprisingly minimal influence on single-core and calmly threaded efficiency.
This flexibility implies that AMD can have its cake and eat it too—and so are you able to. Need each little bit of juice to encode big recordsdata quick? Or maybe that you must set a decrease energy restrict attributable to warmth or energy invoice issues? You’re lined.
AM5 isn’t low cost

Adam Patrick Murray / IDG
The transfer from the long-standing AM4 platform to AM5 is a giant shift that permits blistering pace throughout the board—not only for the processor, however for reminiscence, discrete GPUs, and storage, each now and sooner or later. AM5 works in PCIe 5, DDR5, USB4, and different cutting-edge options that may push correctly geared up PCs to wild new frontiers of efficiency.
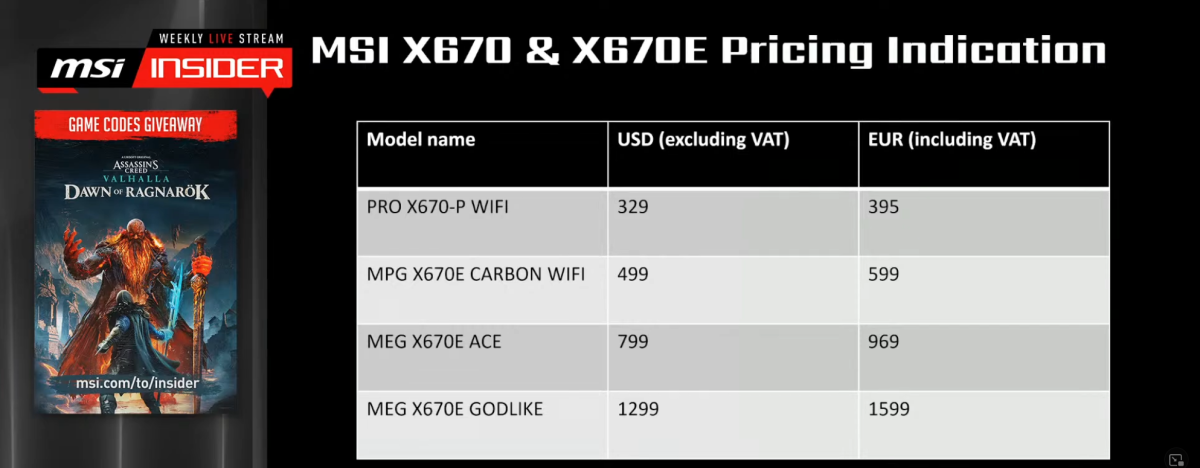
However, that improve comes with a literal value—count on to pay a premium for an AM5 motherboard if constructing a PC at launch. Right now, solely the dearer X670 and X670 Extreme mobos can be found, they usually require fairly an outlay. Take MSI for instance:
MSI / YouTube
You’re seeing that proper: A top-of-the-line MSI X670 Extreme motherboard is a cool $1,299 USD. The most cost-effective X670 possibility is $329.
Other elements will hit exhausting, too. DDR5 reminiscence isn’t low cost—Ryzen 7000’s candy spot for RAM pace is double that of Ryzen 5000’s. Currently you’ll pay about $230 for 32GB of DDR5-6000 memory, whereas 32GB of DDR4-3600 is round $115. And when PCIe 5 SSDs arrive in November, they’ll undoubtedly have extravagant worth tags.
To save no less than some cash, you need to wait till October—the extra reasonably priced B650 and B650 Extreme motherboards launch then.
Running at 95C is ok
Comb by means of web boards, and also you’ll see publish after publish involved about CPUs working above a sure temperature. It’s true that if temps climb too excessive, you may see choked efficiency (often called thermal throttling). Some folks additionally concern shortening their chip’s life span.
But when checking on your processor’s temperature, don’t stress when you see your Ryzen 7000 launch chip sitting at 95 levels Celsius beneath heavy load. These 4 X-class chips can cling on the market with no repercussions, in keeping with AMD. It could also be increased than you may be used to seeing, and maybe you could have different causes you’ll wish to drop that temperature, nevertheless it’s inside spec.
Intel’s 13th-gen Raptor Lake looms massive
Intel
Previous Ryzen generations had loads of respiratory room to luxuriate of their dominance. (The 5950X had a complete 12 months, for instance.)
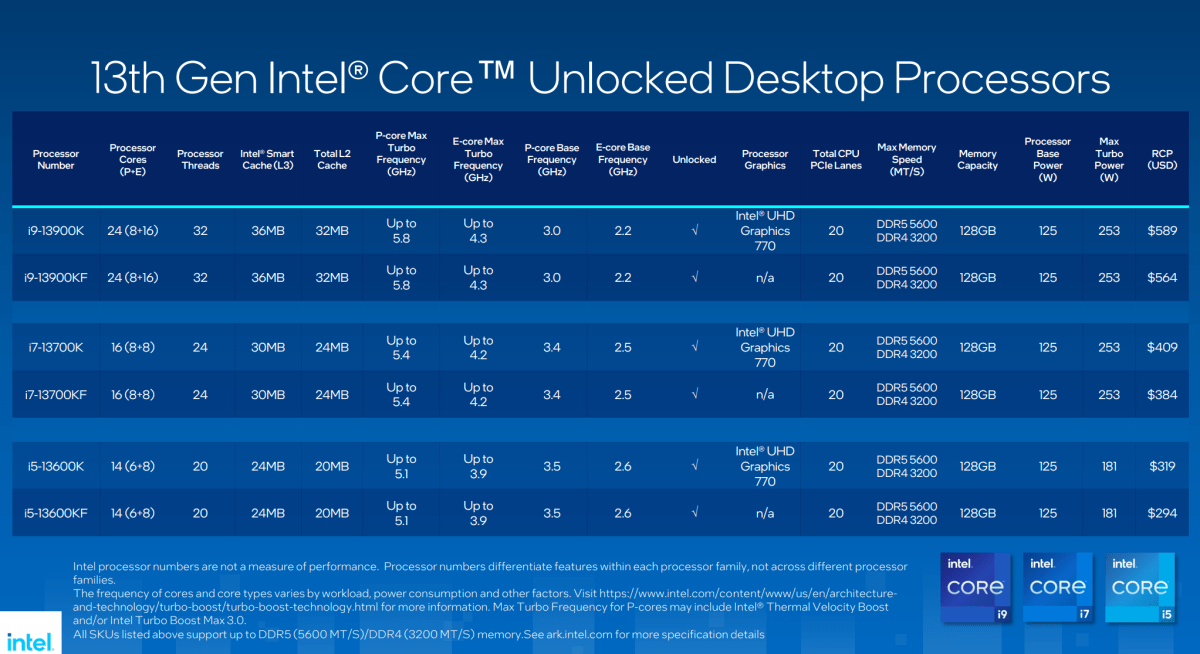
Not Ryzen 7000. On the exact same day it launched, Intel formally introduced its 13th-generation Core processors. In addition to revealing a 24-core, 32-thread flagship chip and screaming quick clock speeds (together with a 6GHz processor coming early next year), Team Blue claimed an as much as 24 p.c enchancment in gaming efficiency over 12th-gen chips. And the brand new Core i9-13900Ok will supply a bump of 15 p.c in single-threaded efficiency and 41 p.c for multithreaded in comparison with the Core i9-12900Ok.
With these numbers, a 13900Ok will probably go evenly toe-to-toe with a 7950X in multithreaded duties, and beat it by about 8 to 10 p.c in single-threaded and lightly-threaded duties (aka gaming).
Intel can also be speaking about its energy effectivity now, too—even regardless of its energy rankings climbing increased than these of Ryzen 7000. At 65 watts, the 13900Ok will have the ability to match 12900Ok’s 241W turbo mode efficiency. That’s a giant assertion.
How the chips fall (ahem) gained’t be clear till Raptor Lake’s launch on October 20th, nonetheless. Until then, there’s a lot to like about Ryzen 7000.
