Widespread use of unpatched open supply code in the most well-liked Android apps distributed by Google Play has prompted vital safety vulnerabilities, suggests an
American Consumer Institute report launched Wednesday.
Thirty-two p.c — or 105 apps out of 330 of the most well-liked apps in 16 classes sampled — averaged 19 vulnerabilities per app, in line with the
report, titled “How Secure Are Fashionable Apps? A Research of Important Vulnerabilities and Why Shoppers Ought to Care.”
Researchers discovered crucial vulnerabilities in lots of widespread purposes, together with a number of the hottest banking, occasion ticket buying, sports activities and journey apps.
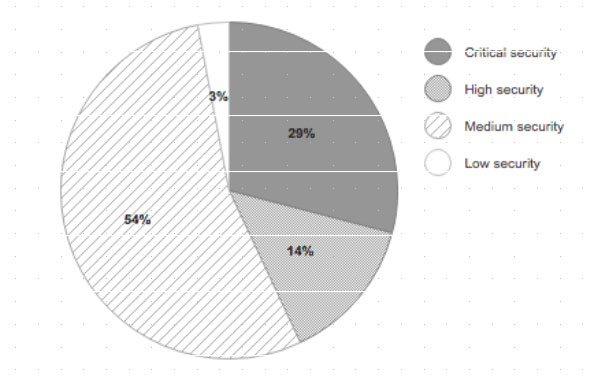
Distribution of Vulnerabilities Based mostly on Safety Threat Severity
ACI, a nonprofit client training and analysis group, launched the report back to spearhead a public training marketing campaign to encourage app distributors and builders to deal with the worsening safety disaster earlier than authorities rules impose controls over Android and open supply code growth, stated Steve Pociask, CEO of the institute.
The ACI will current the report in Washington D.C. on Wednesday, at a public panel attended by congressional committee members and workers. The session is open to the general public.
“There have been 40,000 recognized open supply vulnerabilities within the final 17 years, and one-third of them got here final yr,” ACI’s Pociask informed LinuxInsider. That may be a vital trigger for concern, on condition that 90 p.c of all software program in use right this moment accommodates open supply software program elements.
Pushing the Requirements
ACI determined the general public panel can be a superb venue to start out educating shoppers and the business about safety failings that infect Android apps, stated Pociask. The report is supposed to be a place to begin to find out whether or not builders and app distributors are maintaining with disclosed vulnerabilities.
“We all know that hackers actually are,” Pociask remarked. “In a approach, we’re giving … a highway map to hackers to get in.”
The purpose is to chase away the necessity for eventual authorities controls on software program by making a public dialog that addresses a number of important questions. Given the research’s outcomes, shoppers and legislators must know if app distributors and builders are sluggish to replace due to the expense, or merely complacent about safety.
Different important unanswered questions, in line with Pociask, embody the next: Do the distributors notify customers of the necessity to replace apps? To what extent are prospects updating apps?
Not everybody depends on auto replace on the Android platform, he famous.
“Some distributors outsource their software program growth to suit their funds and do not comply with up on vulnerabilities,” Pociask stated.
Having the federal government step in can produce detrimental penalties, he warned. Generally the options imposed will not be versatile, and so they can discourage innovation.
“It can be crucial for the business to get itself so as relating to privateness necessities, spoofing cellphone numbers and safety points,” stated Pociask.
Report Parameters
Companies battle to supply sufficient safety for client private info and privateness. Governments in California and the European Union have been placing extra aggressive client privateness legal guidelines in place. People have turn into extra conscious of how weak to theft their knowledge is, in line with the report.
One seemingly indispensable gadget that the majority shoppers and companies use is a smartphone. Nevertheless, the apps on it might be one of the crucial severe knowledge and privateness safety dangers, the report notes.
Researchers examined 330 of the most well-liked Android apps on the Google Play Retailer throughout the first week in August. ACI’s analysis crew used a binary code scanner — Readability, developed by Insignary — to look at the APK recordsdata.
Slightly than concentrate on a random sampling of Google Play Retailer apps, ACI researchers reported on the biggest or hottest apps in classes. A lot of the apps are distributed inside the USA. Researchers picked 10 high apps in every of the 33 classes within the Play retailer.
Factoring the Outcomes
Outcomes have been charted as crucial, excessive, medium and low vulnerability scores. Of 330 examined apps, 105 — or 32 p.c — contained vulnerabilities. Of these recognized, 43 p.c both have been crucial or excessive danger, based mostly on the nationwide vulnerability database, in line with the report.
“We based mostly our research on the most well-liked apps in every class. Who is aware of how a lot worse the untested apps are by way of vulnerabilities?” Pociask requested.
Within the apps sampled, 1,978 vulnerabilities have been discovered throughout all severity ranges, and 43 p.c of the found vulnerabilities have been deemed high-risk or crucial. Roughly 19 vulnerabilities existed per app.
The report supplies the names of some apps as examples of the assorted methods distributors take care of vulnerabilities. Important vulnerabilities have been discovered in lots of widespread purposes, together with a number of the hottest banking, occasion ticket buying, sports activities and journey apps.
For instance, Financial institution of America had 34 crucial vulnerabilities, and Wells Fargo had 35 crucial vulnerabilities. Vivid Seats had 19 crucial and 5 excessive vulnerabilities.
Just a few weeks later, researchers retested a number of the apps that originally examined approach out of vary. They discovered that the 2 banking apps had been cleaned up with updates. Nevertheless, the Vivid Seats app nonetheless had vulnerabilities, stated Pociask.
Indications for Cures
Simpler governance is crucial to addressing “threats akin to compromised client units, stolen knowledge, and different malicious exercise together with identification theft, fraud or company espionage,” states the report.
These outcomes more and more have been taking heart stage, famous the researchers.
The ACI research recommends that Android app builders scan their binary recordsdata to make sure that they catch and handle all recognized safety vulnerabilities. The research additionally stresses the urgency and want for apps suppliers to develop greatest practices now, to be able to cut back dangers and stop a backlash from the general public and policymakers.
The researchers highlighted the complacency that many app suppliers have exhibited in failing to maintain their software program adequately protected towards recognized open supply vulnerabilities that go away shoppers, companies and governments open to hacker assaults, with doubtlessly disastrous outcomes.
Word: Google routinely scans apps for malware, but it surely doesn’t oversee the vulnerabilities that would enable them.
“We need to create much more consciousness for the necessity to replace the vulnerabilities shortly and diligently. There’s a must push out the updates and notify shoppers. The industries ought to become involved in defining greatest practices with some kind of recognizable security seal or ranking or certification,” Pociask stated.
App Maker or Person Drawback?
This present ACI report, together with others offering
similar indications about software program vulnerabilities, considerations an space many app customers and distributors appear to disregard. That state of affairs is exacerbated by hackers discovering new methods to trick customers into permitting them entry to their units and networks.
“Posing as actual apps on an accredited platform just like the Google Play Retailer makes this kind of malicious exercise all of the extra dangerous to unsuspecting customers,” stated Timur Kovalev, chief know-how officer at
Untangle.
It’s crucial for app customers to remember that hackers don’t care who turns into their subsequent sufferer, he informed LinuxInsider.
Everybody has knowledge and personal info that may be stolen and bought. App customers should notice that whereas hackers need to acquire entry and management of their units, most additionally will attempt to infiltrate a community that the gadget connects to. As soon as this occurs, any gadget related to that community is in danger, Kovalev defined.
Even when an app maker is conscientious about safety and follows greatest practices, different weak apps or malware on Android units can put customers in danger, famous Sam Bakken, senior product advertising and marketing supervisor at
OneSpan.
“App makers want to guard their apps’ runtime towards exterior threats over which they do not have management, akin to malware or different benign however weak apps,” he informed LinuxInsider.
A part of the Drawback Cycle
The difficulty of unpatched vulnerabilities makes the continuing state of affairs of malicious apps extra troublesome. Malicious apps have been a constant drawback for the Google Play Retailer, stated Chris Morales, head of safety analytics at
Vectra.
In contrast to Apple, Google doesn’t keep strict management over the purposes developed utilizing the Android software program growth package.
“Google used to carry out fundamental checks to validate an app is secure for distribution within the Google Play Retailer, however the scale of apps that exists right this moment and are submitted each day means it has turn into very tough for Google to maintain up,” Morales informed LinuxInsider.
Google has applied new machine studying fashions and methods throughout the previous yr, he identified, in an effort to enhance the corporate’s capability to detect abuse — akin to impersonation, inappropriate content material or malware.
“Whereas these methods have confirmed efficient at decreasing the overall variety of malicious apps within the Google Play Retailer, there’ll at all times be vulnerabilities in utility code that get by Google’s validation,” famous Morales.
Builders nonetheless want to deal with the issue of malicious or weak apps that might be exploited after being put in on a cellular gadget. That may be dealt with by making use of machine studying fashions and methods on the gadget and on the community. That may assist to determine malicious behaviors that may happen after an app is already put in and bypassed the Google safety checks, Morales defined.
Time for Huge Brother?
Having authorities businesses step in to impose options could result in additional issues. Slightly than a one-size-fits-all resolution, ACI’s Pociask prefers a system of priorities.
“Let’s examine if the business can give you one thing earlier than authorities rules are imposed. Getting a knee-jerk response proper now can be the fallacious factor to do by way of imposing an answer,” he cautioned.
Nonetheless, private units are the consumer’s accountability. Customers must take extra accountability almost about what apps they’re permitting on their units, insisted Untangle’s Kovalev.
“Authorities intervention right now is probably going not wanted, as each customers and Google can take extra actions to guard themselves towards malicious apps,” he stated.
Frameworks Exist
Coping with unpatched Android apps could not want large efforts to reinvent the wheel. Two potential beginning factors already can be found, in line with OneSpan’s Bakken.
One is the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology, or NIST. It has pointers for vetting cellular apps, which lay out a course of for making certain that cellular apps adjust to a corporation’s cellular safety requirement.
“This can assist an enterprise, for instance, to maintain some weak cellular apps out of their atmosphere, however instituting such a program is not any small feat. It is also merely steering at this level,” stated Bakken.
The opposite place to begin might be the Federal Establishments Examination Council, or FFIEC, which supplies some steering for examiners to guage a monetary establishment’s administration of cellular monetary providers danger. It additionally supplies some safeguards an establishment ought to implement to safe the cellular monetary providers they provide, together with cellular apps.
“Ultimately, the effectiveness of any authorities intervention actually depends upon enforcement. It is probably that any intervention would concentrate on a particular business or industries, which means not all cellular app genres can be in scope,” Bakken stated. “That implies that builders of some cellular apps for shoppers wouldn’t essentially have any incentive to safe their apps.”
What Must Occur?
One main resolution focuses on patching the Google Play platform. Becoming a member of the platform is simple, in line with Kovalev. Builders full 4 fundamental steps and pay a charge.
As soon as joined, builders can add their apps. Google processes them by a fundamental code examine. Usually, malicious apps don’t look like malicious, as they’ve been programmed with a time-delay for malicious code to be executed, he famous.
“To fight these malicious apps, Google has begun to implement higher vetting methods — like AI studying and offering rewards to white hat professionals who search out and floor these malicious apps,” Kovalev stated.
Whereas these methods have helped to pinpoint malicious apps, the apps ought to be vetted extra completely previous to being publicly obtainable to unsuspecting customers, he careworn.
Closing Resolution
The final word repair for damaged Android apps rests with app makers themselves, OneSpan’s Bakken stated. They’re in the most effective place to steer the cost.
He supplied this guidelines for cellular app builders:
- Do menace modeling and embody safety in product necessities.
- Present safe code coaching to Android builders.
- Do safety testing of their apps regularly as a part of the event cycle.
- Repair recognized vulnerabilities as they go.
- Submit their apps to penetration testing previous to launch.
“After which, lastly, they need to proactively strengthen their app with app-shielding know-how that features runtime safety,” Baken stated, “so the app itself is protected, even in untrusted and doubtlessly insecure cellular environments, to mitigate exterior threats from malware and different weak apps.”
![]()
<!–////–>
 Jack M. Germain has been an ECT Information Community reporter since 2003. His foremost areas of focus are enterprise IT, Linux and open supply applied sciences. He has written quite a few critiques of Linux distros and different open supply software program.
Jack M. Germain has been an ECT Information Community reporter since 2003. His foremost areas of focus are enterprise IT, Linux and open supply applied sciences. He has written quite a few critiques of Linux distros and different open supply software program.