With any luck, Arm’s new Lumex CPU platform could give us a touch at what to anticipate for upcoming Windows on Arm PCs: 4 tiers of CPU energy, plus an improved ray-tracing engine and graphics upscaling.
Arm says that its new Lumex C1-series chips will ship 25 % extra efficiency than the Cortex X925 series of processors it launched in May 2024. Like the X925, the newest Lumex C1 cores are being optimized with 3nm course of applied sciences in thoughts, with bodily implementations and foundry collaborations to hurry clients to market.
(While Arm has hinted at constructing its personal bodily cores for years, nevertheless, firm representatives would say solely that it consists of “near production-ready physical implementations for partners” and is “not a chip.”)
The Lumex platform is Arm’s model for smartphones. PC-specific Arm chips can be branded as “Niva” below Arm’s new naming scheme, although they are going to share some widespread options with the Lumex cores. Qualcomm, which truly makes the Arm processors, makes use of the “Snapdragon” model, which is able to virtually actually proceed.
Arm chips energy the overwhelming majority of the world’s smartphones, as Arm licenses its designs to clients who can select to convey the Arm cores to market or take an architectural license and design suitable however in any other case model new designs of their very own making. That’s the method Apple and Qualcomm have taken — who, along with designing smartphones, have introduced Arm into the Mac OS house in addition to Windows on Arm PCs. Though Qualcomm and Arm have had their legal differences over licensing Arm’s cores — which have since been settled — an Arm consultant declined to remark when requested if any ongoing authorized points would forestall Qualcomm from taking a license.
Arm
And you’ll, apparently, see the Lumex in additional than simply PCs. “So the Lumex platform is going to power flagship smartphones through to PCs and tablets,” mentioned James McNiven, the vice chairman of product administration for Arm, in a press briefing.
Smartphones, although, have their very own calls for: low energy, which Arm’s RISC structure was designed for; and maximizing native AI. The Cortex C1 sequence consists of what Arm calls Scalable Matrix Extension 2 (SME2), utilizing the Arm v9.3 instruction set.
Arm doesn’t use a devoted NPU. Instead, it makes use of a know-how referred to as KleidiAI that primarily makes use of software program libraries to deal with AI-specific capabilities contained in the CPU, irrespective of which model of the Arm structure is current. In the C1 CPU cluster, Arm says, you’ll see a 5X uplift in AI efficiency.
Arm says that may enhance efficiency on apps that at all times have some type of AI know-how operating, similar to audio technology, digicam inferencing, or laptop imaginative and prescient. Specifically, Arm is claiming over 4.7 instances enchancment in latency, speech recognition, and classical massive language mannequin duties, and about 2.8 instances sooner audio technology.
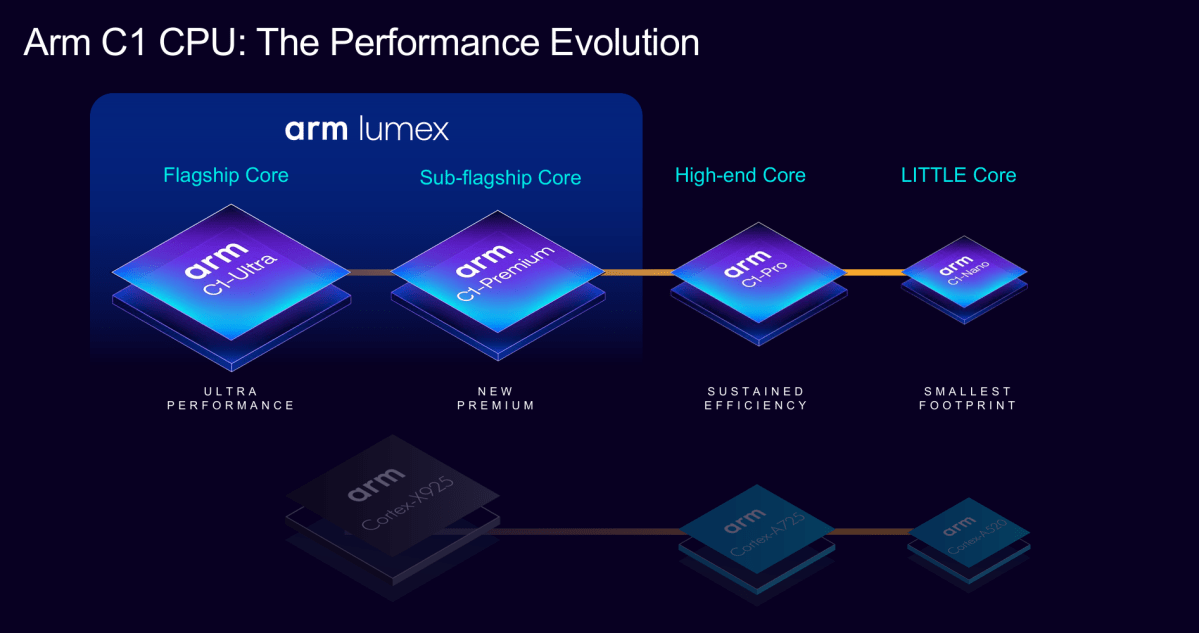
The different factor Arm has been identified for is that it principally pioneered the idea of efficiency and effectivity cores, a technique often known as “Big-Little.” But with the Lumex, that’s been taken to a brand new stage with the addition of a brand new “premium” core. Now, there are 4 totally different tiers of CPU cores: the C1-Ultra, the C1-Premium, the C1-Pro, and the C1-Nano.
Arm
Nothing’s actually modified all that a lot: The Ultra and Premium cores are merely two tiers of “performance” cores, whereas the Pro and Nano ship totally different ranges of effectivity. Arm executives mentioned that the Premium core might stand in for the Ultra cores on non-flagship, cheaper gadgets, because it affords related efficiency to the Ultra, however in a 35 % smaller space. The C1 Pro “improves” upon the Cortex A75 by way of efficiency and effectivity, McNiven mentioned, whereas the Nano has the “smallest footprint” and can play a job in each flagship and entry-level gadgets, he mentioned. Overall, Arm executives mentioned that the on-device AI is thrice extra energy environment friendly than the earlier implementations, and the Pro is 12 % extra energy environment friendly on the similar frequency.
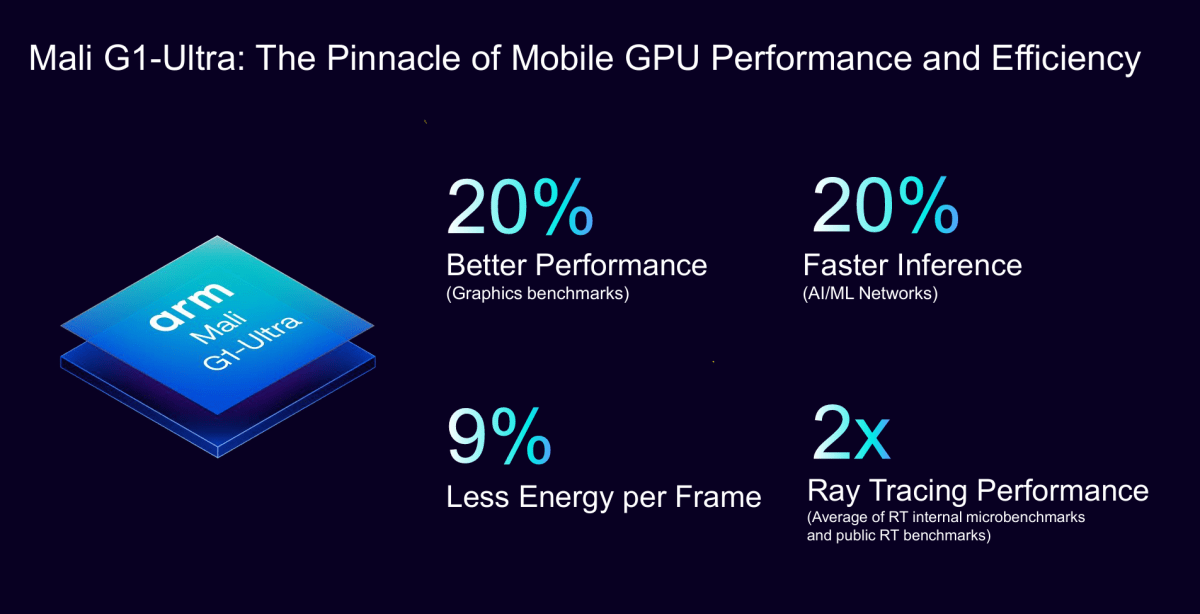
Arm can be introducing a brand new GPU, the Mali G1-Ultra, which is able to promise 20 % higher graphics efficiency, twice the ray-tracing efficiency, and 20 % sooner inferencing for AI processing than the sooner Immortalis-G925. The Mali G1-Ultra will even devour much less energy, because the block is by itself energy island with much less leakage when idle.
Specifically, Arm is claiming that body charges on ray-traced video games can be 40 % increased than its predecessor, a part of transferring to a “single-ray” mannequin for improved effectivity and extra sensible lighting,” McNiven mentioned. The new Mali core additionally consists of upscaling — rapidly rendering at a decrease decision for improved body fee, then upscaling it for higher visible high quality — nevertheless it doesn’t use the AI-generated frames of some desktop GPUs.
Arm
“One of the examples that we have been seeing recently was some of the new ray tracing benchmarks like [UL’s 3DMark] Solar Bay Extreme, and I think that we see there up to a doubling in performance, because it is so ray tracing heavy. So it really does depend on just the amount of ray-tracing content,” McNiven mentioned.
One concept behind the Lumex platform, executives mentioned, was to maneuver sure cloud-based AI capabilities on to the machine. Specifically, a big language mannequin on the planet of Krafton’s Inzoi (a non secular successor to The Sims) was run on-device on the GDC convention, they mentioned, in addition to a “coach” that watched you play in Tencent’s Honor of Kings and supplied recommendation. A serious on-line fee supplier can be working to place agentic AI on machine to deal with fee processing throughout peak instances, as an alternative of committing to costly, back-end cloud servers, mentioned Chris Bergey, the senior vice chairman of the shopper line of enterprise at Arm.
“If your device is capable of running a large language model, you have an extra means of interacting with the game that augments your experience,” McNiven mentioned. “But if you don’t have it, the game is still playable.”
