Debian works itself or in derivatives similar to Open Media Vault or Raspberry Pi OS as a secure and lean server system on numerous private and non-private gadgets.
However, anybody in search of a classy and beginner-friendly desktop is not going to consider Debian first. This is because of unprocessed software program, together with the respective consumer interface, which all the time comes as an unique upstream from the producer (similar to Gnome or KDE).
In addition, there are Debian peculiarities that irritate Linux newcomers, but in addition these switching from Ubuntu techniques. Even the installer desires to know far more from the consumer than with Ubuntu or Mint. More elementary, nonetheless, is the extraordinarily conservative launch mannequin, which doesn’t present for any kernel updates or purposeful software program updates for 2 full years.
Setup with small however some hurdles
Even the seek for the Debian set up medium requires a minimal data of Linux terminology. The web site debian.org isn’t tough to seek out, however when you merely click on on “Download” right here, you’ll obtain the Netinstaller with no stay system.
This is unsuitable for pre-testing with a desired desktop. The subpage debian.org/distrib turns a number of data right into a complicated search sport, particularly the redirection to the worldwide “Download mirrors”.
If newcomers don’t load Debian with the specified desktop right here, that is comprehensible, however can often nonetheless be corrected within the installer.
Debian has plenty of system peculiarities and delivers desktops unprocessed. The setup due to this fact requires some changes – for Gnome, for instance, with the Gnome-shell-extension-manager.
Gnome Extension Manager
The installer asks considerably extra questions than Ubuntu. Most of them will not be crucial: area and proxy can merely be skipped; the basis account, which is unfamiliar to many, is obligatory right here, and with partitioning (with plenty of specialties) you will get away with the straightforward default settings, offered Debian solo is allowed to take over the info provider.
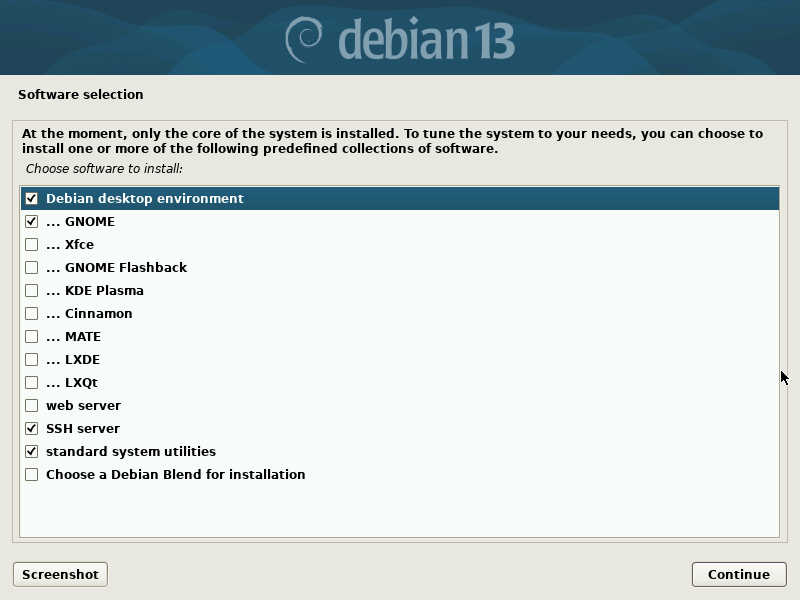
Answering “Yes” to the query “Use network mirror?” can right any obtain mishaps, as a result of this then permits one other “software selection”. It’s all the time advisable to pick the “Debian desktop environment” choice and likewise a desktop similar to Gnome or KDE.
Without a desktop, solely the substructure is accessible, however the system is headless. Without the “environment”, the chosen desktop is accessible, however no desktop software program (browser, sound, cups, and community supervisor might also be lacking).
The launch coverage
Debian prioritizes stability on the expense of up-to-datedness. A brand new Debian model is launched roughly each two years (presently Debian 13) and receives three years of assist. During this era, there are solely common safety updates—the kernel and software program (together with the desktop) stay on the identical degree.
Experienced customers can circumvent this by together with backport sources, however by default Debian software program stays fastened for at the very least two years. This is the alternative of the agile rolling mannequin of Arch Linux, and Ubuntu can be comparatively progressive with its biannual updates (level releases with kernel upgrades).
The Debian installer presents this alternative within the “Netinst” variant, but in addition with stay set up media, offered the “Network mirror” choice is activated.
LinuxTechi
Release upgrades to the following increased model after two years are technically provided to customers, however will not be automated. The consumer should substitute the previous launch identify (e.g. “bookworm”) with the brand new one (e.g. “trixie”) within the “/etc/apt/sources. list” file every time it happens (at the very least 3 times) after which carry out an improve with
sudo apt full-upgradeto request an replace. This isn’t rocket science, nevertheless it’s totally different from the straightforward click on supply in an Ubuntu “update manager”.
Debian is in good fingers on computer systems the place no new {hardware} elements are anticipated for years. By “components” we imply crucial candidates similar to graphics playing cards or CPUs that will require newer kernels or graphics libraries.
Debian desktop customers also needs to be unconcerned about lacking out on two years of latest options in Gimp, VLC, or Gnome.
Debian peculiarities
Debian doesn’t acknowledge “sudo” for easy account adjustments. For administrative duties, “su” ought to be used to modify to root, whose password was outlined throughout set up. If you need Ubuntu situations, you’ll be able to set up sudo (and visudo) within the root account:
apt set up sudoThe foremost consumer can then be added to the sudo group.
usermod -aG sudo seppThis results in the following peculiarity: “usermod” appears to be lacking like all typical admin instructions. The background to it is a restrictive path specification: directories similar to “/sbin” or “/usr/sbin” with the system administration instruments will not be included within the default path.
A command similar to “usermod” will due to this fact solely work with the entire path “/sbin/usermod”. In steady operation, it’ll be simpler so as to add the PATH variable accordingly (“export PATH=[…]:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin”).
After a Debian set up, the file “/etc/apt/sources.list” typically comprises the road “deb cdrom […]” (the set up ISO picture) because the package deal supply, which results in errors with each apt command. The line should due to this fact be commented out or deleted.
Such minor points are straightforward to repair, however can initially irritate Ubuntu customers significantly. Service configurations are additionally a bit of extra restrictive beneath Debian than beneath Ubuntu distributions.
By default, Debian solely accepts its personal, basic DEB sources as package deal sources: External PPAs will not be permitted, snaps and flatpaks may be optionally retrofitted—as in every single place else—however they aren’t normal.
Desktop, drivers and software program
As with Arch, the chosen desktop comes within the default unique model. Debian gives a couple of of its personal background photographs, however nothing extra. Depending on the desktop, you’ll need to make your individual enhancements right here—actually extra with Gnome than with KDE or XFCE, for instance.
This isn’t a drawback in precept, however assumes that you’re acquainted with desktop extensions, desktop settings and themes, and are joyful to hold out such customizations your self.

Typical for Debian: Firefox ESR, which is just up to date (functionally) yearly, is pre-installed because the default browser.
Sam Singleton
With regard to proprietary drivers and firmware, Debian has relaxed its beforehand restrictive stance in order that “nonfree” sources are actually robotically permitted. GPU drivers (similar to “nvidia-driver”), graphics libraries (similar to “mesa-utils”), or codecs (similar to “ffmpeg”) can due to this fact be put in instantly or are already added throughout set up.
Software and kernels are solely fairly up-to-date in brand-new Debian variations and stay at this degree.
Typical for conservative software program can be the usage of Firefox ESR as the usual browser, which additionally receives operate updates as an exception, however solely yearly.
Debian-like options
No query: Compared to Ubuntu & co., Debian requires plenty of steps to arrange the system and desktop. Compared to Arch Linux, nonetheless, the hassle is restricted.
If you continue to wish to keep away from these steps however wish to use the rock-solid Debian, you’ll be able to swap to derivatives similar to MX Linux with XFCE or Q4-OS with KDE.
The Debian by-product that ensures the closest attainable proximity to Ubuntu is the Mint variant Linux Mint LMDE.
