How it may be that two Intel 11th-gen Tiger Lake pocket book PCs, with precisely the identical chip inside, can provide efficiency that differs by as much as 37 p.c? And extra importantly, how will you inform the distinction?
The brief reply is: You can’t. An unlucky facet impact of how Intel develops processors like Tiger Lake will make it tougher for customers to find out the precise efficiency of a laptop computer simply by studying an inventory of its options, and it’ll most likely get tougher over time.
The downside is that Intel is designing cellular microprocessors like Tiger Lake to permit laptop computer makers higher flexibility in how they select to “clock” them, or at what frequency they’re assigned to run. A laptop computer that makes use of a selected processor might run 37 p.c sooner than a second laptop computer that features precisely the identical chip, Intel executives say.
That means laptop computer patrons must look tougher at precise efficiency critiques with comparative knowledge to know what they’re getting.
The downside truly cropped up earlier, as Intel moved into its prior (10th-gen) Ice Lake chips. But Intel executives highlighted it throughout its Tiger Lake launch as one thing to be careful for. And all of it goes again to how laptop computer microprocessors have developed over time.
This column in Intel’s “Tiger Lake” record of processors is a delicate tipoff that Intel has moved away from its restricted thermal-design-power metric that has existed for many years.
No mounted frequencies
Traditionally, chips have carried thermal design energy (TDP) specs, defining the ability draw and clock speeds at which the chip might safely function with out overheating. Laptops needed to handle and typically throttle their energy calls for to maintain the chip inside sure thermal limits. If a chip exceeded that for some purpose, the laptop computer might throw errors or crash.
Over time, Intel (and AMD) started including “turbo” capabilities, permitting the chip to exceed its rated voltage via overclocking for a short while, till a danger of overheating pressured it to decelerate but once more. Intel processors now sometimes present single-core turbo modes, all-core turbo modes, and even cherry-pick choose cores for overclocking duties.
Notebooks sometimes don’t run at a set frequency, however bounce up and down relying on the demand. Some name the usual degree PL1 and the turbo mode PL2, and consult with a 3rd quantity, tau, because the time a processor core can spend in a boosted state.
With Tiger Lake, Intel has stopped defining its chips when it comes to thermal design energy, now defining simply an “operating range” in watts, defined Ryan Shrout, chief efficiency strategist for Intel and senior director of consumer technical advertising and marketing. Intel’s Tiger Lake chips designed for laptops (the UP3 household), now have an working vary from 12 to 28 watts. That offers a laptop computer maker the choice of transport a lower-performance 15W pocket book that emphasizes lengthy battery life, or working it at 28W to commerce battery life for higher efficiency.
 Intel
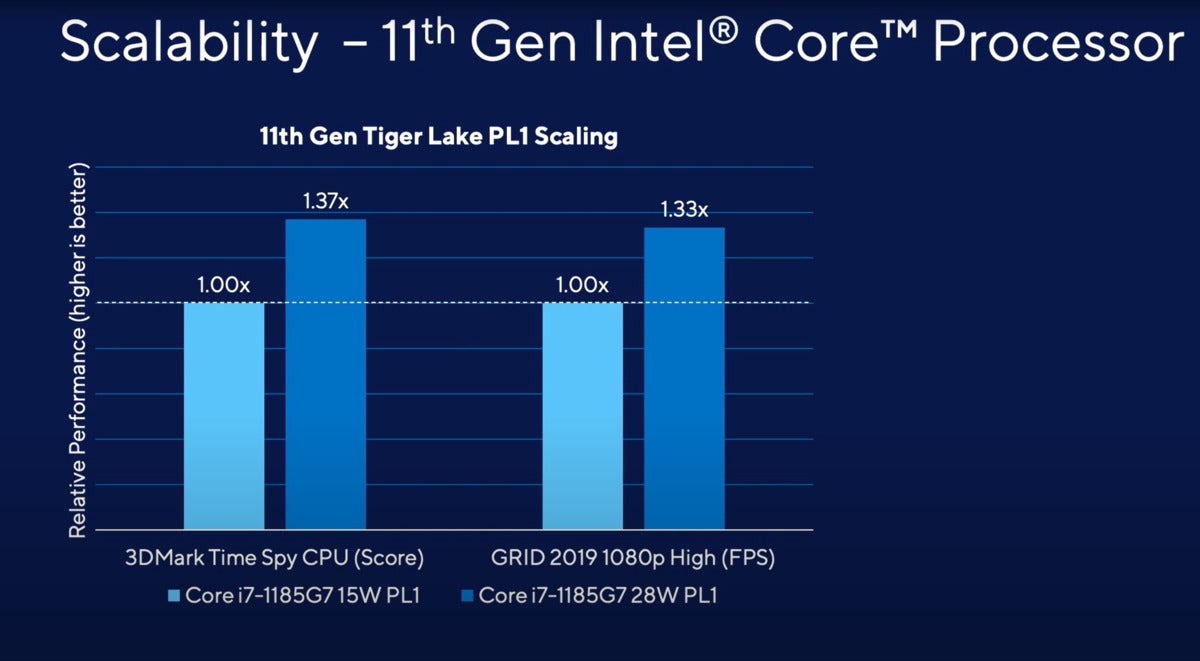
IntelDepending on how the laptop computer is configured, a Tiger Lake chip can fluctuate broadly in efficiency.
Under these new working ranges, Shrout stated, you can purchase a laptop computer with a Core i7-1185G7 chip inside, configured by the seller to eat 15 watts. It would run a recreation like Grid 2019, a racing recreation, at a given body price. But a second laptop computer with an equivalent Core i7-1185G7 chip inside, configured to run at 28 watts, would run the sport 33 p.c sooner.
How quick is my laptop computer? Only testing will inform
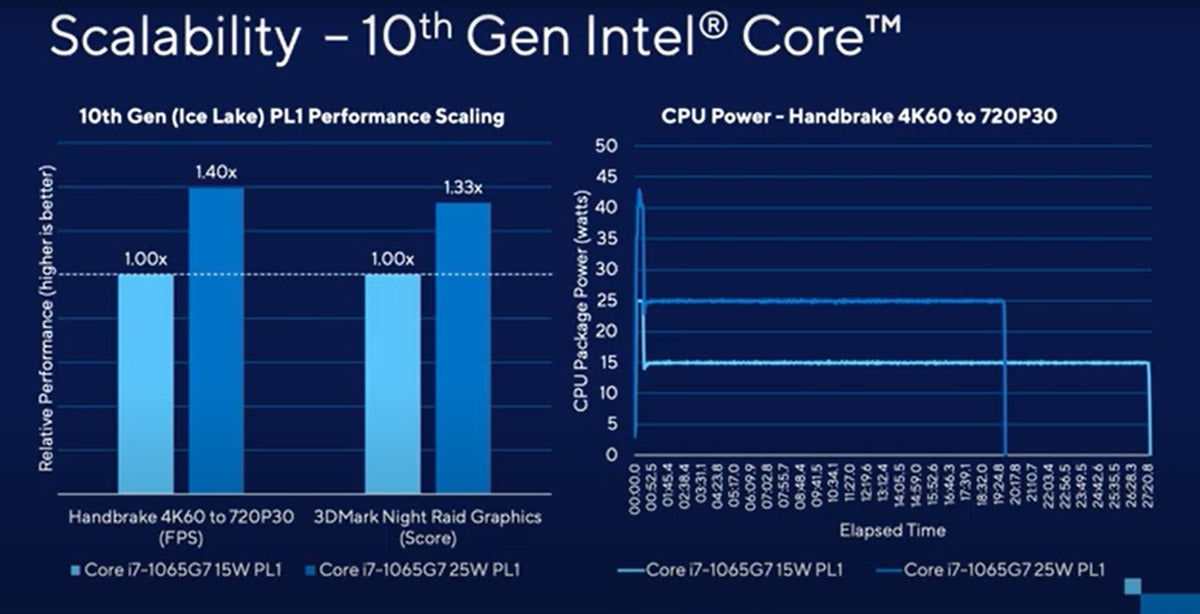
The identical problem existed within the prior Ice Lake era, however it was extra pronounced, as Shrout confirmed in check knowledge shared at a press briefing. At proper under are check outcomes utilizing the CPU-centric HandBrake conversion utility. A Core i7-1065G7 working at 15 watts might, in turbo mode, briefly sustain with the identical chip working at 25 watts in a non-turbo PL1 state.
 Intel
IntelThe downside existed within the 10th-gen “Ice Lake” era, however the trade nonetheless isn’t doing something about it. Again, the identical chip is being in contrast at completely different energy ranges.
Otherwise, in that check and others (see bar charts at left above), there was as much as a 40-percent efficiency distinction. And that’s completely acceptable, Shrout stated.
“The TDP is the same on the spec sheet for these different systems, but because of the cooling implementation, the tuning from the OEMs and the partnership from Intel, and the target audience and the use cases of these systems, the performance can actually be quite different across different workloads,” Shrout stated.
“No single design is best in our view, but each design allows for different focuses, and product design choices,” Shrout stated.
In this case, nonetheless, the pursuits of customers and laptop computer makers are at odds. Laptop makers get the flexibleness, however customers get no perception into whether or not their laptop computer is working at a decrease or greater efficiency state.
“The power of Tiger Lake is its scalability, and the dynamic range of the product,” Shrout stated. “We don’t enforce some kind of branding indication, or what thermal design, or what power delivery design,” Shrout stated. “So it really will come down to the performance reviews and narratives to determine what you’re running at.”
 Intel
IntelIntel is making the argument that the identical Tiger Lake chip is definitely being utilized in a spread of gadgets from tablets via gaming PCs, simply packaged barely otherwise and at completely different energy ranges.
Shrout stated that Intel didn’t plan to tell apart additional at what energy state a chip would run. Intel makes use of a Core i3/i5/i7/i9 branding construction to inform customers what efficiency to count on from its varied product households, and it’s launched its “Evo” brand to point premium notebooks. Consumers and reviewers are free to make use of varied software program instruments to find out a pocket book’s energy settings, Shrout stated, whilst he inspired clients to maintain their eyes on the prize.
“At the end of the day, the performance is what matters most,” Shrout stated.
It’s simply that, as Intel admits, you received’t know what kind of efficiency to count on till that laptop computer is examined.
Related Intel Tiger Lake tales:

